GlucaGen for Diabetics - GlucaGen Full Prescribing Information
Brand Name: GlucaGen
Generic Name: Glucagon Hydrochloride
Contents:
Description
Pharmacology
Indications and Usage
Contraindications
Warnings
Precautions
Adverse Reactions
Overdose
Dosage and Administration
Stability and Storage
How Supplied
Information for Patients
GlucaGen, glucagon hydrochloride, patient information (in plain English)
Description
GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection) manufactured by Novo Nordisk A/S is produced by expression of recombinant DNA in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae vector with subsequent purification.
The chemical structure of the glucagon in GlucaGen® is identical to naturally occurring human glucagon and to glucagon extracted from beef and pork pancreas. Glucagon with the empirical formula of C153H225N43O49S, and a molecular weight of 3483, is a single-chain polypeptide containing 29 amino acid residues. The structure of glucagon is:

GlucaGen® 1 mg (1 unit) is supplied as a sterile, lyophilized white powder in a 2 ml vial, alone, or accompanied by Sterile Water for Reconstitution (1 ml) also in a 2 ml vial (10 pack or diagnostic kit). It is also supplied as a HypoKit with a disposable prefilled syringe containing 1 ml Sterile Water for Reconstitution. Glucagon, as supplied at pH 2.5-3.5, is soluble in water.
Active Ingredient in each vial
Glucagon as hydrochloride 1 mg (corresponding to 1 unit).
Other Ingredients
Lactose monohydrate (107 mg)
When the glucagon powder is reconstituted with Sterile Water for Reconstitution (if supplied) or with Sterile Water for Injection, USP, it forms a solution of 1 mg (1 unit)/ml glucagon for subcutaneous (sc), intramuscular (im), or intravenous (iv) injection.
GlucaGen® is an antihypoglycemic agent, and a gastrointestinal motility inhibitor.
Clinical Pharmacology
Intramuscular (im) injection of GlucaGen® resulted in a mean Cmax (CV%) of 1686 pg/ml (43%) and median Tmax of 12.5 minutes. The mean apparent half-life of 45 minutes after im injection probably reflects prolonged absorption from the injection site. Glucagon is degraded in the liver, kidney, and plasma.1
Antihypoglycemic Action:
Glucagon induces liver glycogen breakdown, releasing glucose from the liver. Blood glucose concentration rises within 10 minutes of injection and maximal concentrations are attained at approximately a half hour after injection (see Figure). Hepatic stores of glycogen are necessary for glucagon to produce an antihypoglycemic effect.
Recovery from insulin induced hypoglycemia (mean blood glucose) after im injection of 1 mg GlucaGen® in Type I diabetic men
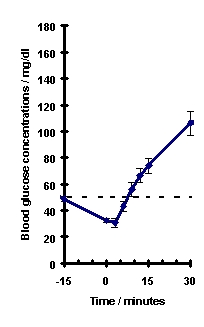
Gastrointestinal Motility Inhibition: Extra hepatic effects of glucagon include relaxation of the smooth muscle of the stomach, duodenum, small bowel, and colon.
Indications and Usage
For the treatment of hypoglycemia:
GlucaGen® is used to treat severe hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) reactions which may occur in patients with diabetes treated with insulin. Because GlucaGen® depletes glycogen stores, the patient should be given supplemental carbohydrates as soon as he/she awakens and is able to swallow, especially children or adolescents. Medical evaluation is recommended for all patients who experience severe hypoglycemia.
For use as a diagnostic aid:
GlucaGen® is indicated for use during radiologic examinations to temporarily inhibit movement of the gastrointestinal tract. Glucagon is as effective for this examination as are the anticholinergic drugs. However, the addition of the anticholinergic agent may result in increased side effects. Because GlucaGen® depletes glycogen stores, the patient should be given oral carbohydrates as soon as the procedure is completed.
Contraindications
Glucagon is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to glucagon or any constituent in GlucaGen® and in patients with pheochromocytoma or with insulinoma.
Warnings
GlucaGen® should be administered cautiously to patients suspected of having pheochromocytoma or insulinoma. Secondary hypoglycemia may occur and should be countered by adequate carbohydrate intake following glucagon treatment.
Glucagon may release catecholamines from pheochromocytomas and is contraindicated in patients with this condition.
Allergic reactions may occur and include generalized rash, and in rare cases anaphylactic shock with breathing difficulties, and hypotension. The anaphylactic reactions have generally occurred in association with endoscopic examination during which patients often received other agents including contrast media and local anesthetics. The patients should be given standard treatment for anaphylaxis including an injection of epinephrine if they encounter respiratory difficulties after GlucaGen® injection.
Precautions
General
In order for GlucaGen® treatment to reverse hypoglycemia, adequate amounts of glucose must be stored in the liver (as glycogen). Therefore, GlucaGen® should be used with caution in patients with conditions such as prolonged fasting, starvation, adrenal insufficiency or chronic hypoglycemia because these conditions result in low levels of releasable glucose in the liver and an inadequate reversal of hypoglycemia by GlucaGen® treatment. Caution should be observed when glucagon is used in diabetic patients or in elderly patients with known cardiac disease to inhibit gastrointestinal motility.
Information for Patients
Refer patients and family members to the "INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS" for instructions describing the method of preparing and injecting GlucaGen®. Advise the patient and family members to become familiar with the technique of preparing glucagon before an emergency arises. Instruct patients to use 1 mg for adults or ½ the adult dose (0.5 mg) for children weighing less than 55 lbs (25 kg). To prevent severe hypoglycemia, patients and family members should be informed of the symptoms of mild hypoglycemia and how to treat it appropriately. Family members should be informed to arouse the patient as quickly as possible because prolonged hypoglycemia may result in damage to the central nervous system. Patients should be advised to inform their physician when hypoglycemic reactions occur so that the treatment regimen may be adjusted if necessary.
Laboratory Tests
Blood glucose measurements may be considered to monitor the patient's response.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been performed. Several studies have been conducted to evaluate the mutagenic potential of glucagon. The mutagenic potential tested in the Ames and human lymphocyte assays, was borderline positive under certain conditions for both glucagon (pancreatic) and glucagon (rDNA) origin. In vivo, very high doses (100 and 200 mg/kg) of glucagon (both origins) gave a slightly higher incidence of micronucleus formation in male mice but there was no effect in females. The weight of evidence indicates that GlucaGen® is not different from glucagon pancreatic origin and does not pose a genotoxic risk to humans.
GlucaGen® was not tested in animal fertility studies. Studies in rats have shown that pancreatic glucagon does not cause impaired fertility.
Pregnancy - Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies were performed in rats and rabbits at GlucaGen® doses of 0.4, 2.0, and 10 mg/kg. These doses represent exposures of up to 100 and 200 times the human dose based on mg/m2 for rats and rabbits, respectively, and revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when GlucaGen® is administered to a nursing woman.
No clinical studies have been performed in nursing mothers, however, GlucaGen® is a peptide and intact glucagon is not absorbed from the GI tract. Therefore, even if the infant ingested glucagon it would be unlikely to have any effect on the infant. Additionally, GlucaGen® has a short plasma half-life thus limiting amounts available to the child.
Pediatric use
For the treatment of hypoglycemia: The use of glucagon in pediatric patients has been reported to be safe and effective.
For use as a diagnostic aid: Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
Adverse Reactions
Severe side effects are very rare, although nausea and vomiting may occur occasionally especially with doses above 1 mg or with rapid injection (less than 1 minute).1 Hypotension has been reported up to 2 hours after administration in patients receiving GlucaGen® as premedication for upper GI endoscopy procedures. Glucagon exerts positive inotropic and chronotropic effect and may, therefore, cause tachycardia and hypertension. Adverse reactions indicating toxicity of GlucaGen® have not been reported. A transient increase in both blood pressure and pulse rate may occur following the administration of glucagon. Patients taking ß-blockers might be expected to have a greater increase in both pulse and blood pressure, an increase of which will be transient because of glucagon's short half-life. The increase in blood pressure and pulse rate may require therapy in patients with pheochromocytoma or coronary artery disease. (see OVERDOSAGE).
Allergic reactions may occur in rare cases. (see WARNINGS).
Overdose
Signs and Symptoms
No reports of overdosage with GlucaGen® have been reported. It is expected, if overdosage occurred, that the patient may experience nausea, vomiting, inhibition of GI tract motility, increase in blood pressure and pulse rate.1 In case of suspected overdosing, the serum potassium may decrease and should be monitored and corrected if needed.
The IV and SC LD50 for GlucaGen® in rats and mice ranges from 100 to greater than 200 mg/kg body weight.
Treatment
Standard symptomatic treatment may be undertaken if overdosage occurs. If the patient develops a dramatic increase in blood pressure, 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine mesylate has been shown to be effective in lowering blood pressure for the short time that control would be needed. It is unknown whether GlucaGen® is dialyzable, but such a procedure is unlikely to provide any benefit given the short half-life and nature of the symptoms of overdose.
Dosage and Administration
Directions for treatment of severe hypoglycemia:
Using the supplied prefilled syringe, carefully insert the needle through the rubber stopper of the vial containing GlucaGen® powder and inject all the liquid from the syringe into the vial. Roll the vial gently until powder is completely dissolved and no particles remain in the fluid. The reconstituted fluid should be clear and of water-like consistency. The reconstituted GlucaGen® gives a concentration of approximately 1 mg/ml glucagon. The reconstituted GlucaGen® should be used immediately after reconstitution. Discard any unused portion. Inject 1 ml (adults and children, weighing more than 55 lbs) or ½ ml (children weighing less than 55 lbs) subcutaneously (s.c), intramuscularly (i.m), or intravenously (i.v). If the weight is not known: Children younger than 6 to 8 years should be given half dose (= ½ ml) and children older than 6 to 8 should be given the adult dose (1ml). Emergency assistance should be sought if the patient fails to respond within 15 minutes after subcutaneous or intramuscular injection of glucagon. The glucagon injection may be repeated while waiting for emergency assistance.1 Intravenous glucose MUST be administered if the patient fails to respond to glucagon. When the patient has responded to the treatment, give oral carbohydrate to restore the liver glycogen and prevent recurrence of hypoglycemia.
Directions for use as a diagnostic aid:
GlucaGen® should be reconstituted with the supplied 1 ml of Sterile Water for Reconstitution (if supplied) or 1 ml Sterile Water for Injection, USP. Using a syringe, withdraw all of the Sterile Water for Reconstitution (if supplied) or 1 ml Sterile Water for Injection, USP and inject into the GlucaGen® vial. Roll the vial gently until powder is completely dissolved and no particles remain in the fluid. The reconstituted fluid should be clear and of water-like consistency. The reconstituted GlucaGen® gives a concentration of approximately 1 mg/ml glucagon. The reconstituted GlucaGen® should be used immediately after reconstitution. Discard any unused portion. When the diagnostic procedure is over, give oral carbohydrate to restore the liver glycogen and prevent occurrence of secondary hypoglycemia.
References for diagnostic aid use only:
| Time of maximal glucose concentration | Time for GI smooth muscle relaxation |
| Intravenous: 5 to 20 minutes | Intravenous: 0.25 to 2 mg (IU) - 45 seconds |
| Intramuscular: 30 minutes Subcutaneous: 30 to 45 minutes | Intramuscular: 1 mg (IU) - 8 to 10 minutes 2 mg (IU) - 4 to 7 minutes |
Duration of action -
Hyperglycemic action - 60 to 90 minutes
Smooth muscle relaxation -
Intravenous:
0.25 to 0.5 mg (IU) - 9 to 17 minutes
2 mg (IU) - 22 to 25 minutes
Intramuscular:
1 mg (IU) - 12 to 27 minutes
2 mg (IU) - 21 to 32 minutes
Stability and Storage
Before Reconstitution:
The GlucaGen® package may be stored up to 24 months at controlled room temperature 20o to 25o C (68o to 77o F) prior to reconstitution. Avoid freezing and protect from light. GlucaGen® should not be used after the expiry date on the vials.
After Reconstitution:
Reconstituted GlucaGen® should be used immediately. Discard any unused portion. If the solution shows any sign of gel formation or particles, it should be discarded.
How Supplied
GlucaGen® HypoKit includes:
1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
1 disposable syringe containing 1 ml Sterile Water for Reconstitution
NDC 0169-7065-15
OR
GlucaGen® Diagnostic Kit includes:
1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
1 vial containing 1ml Sterile Water for Reconstitution
NDC 55390-004-01
OR
The GlucaGen® 10-pack includes:
10x1 vial containing 1 mg (1 unit) GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
NDC 55390-004-10
Information for Patients
GlucaGen® HypoKit
Emergency Use for Low Blood Sugar
(glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection) 1 mg.
BECOME FAMILIAR WITH THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE AN EMERGENCY ARISES. DO NOT USE THIS PACKAGE AFTER THE EXPIRATION DATE. IF YOU HAVE QUESTIONS CONCERNING THE USE OF THIS PRODUCT, CONSULT A DOCTOR, NURSE, OR PHARMACIST.
Make sure that your relatives or close friends know that if you become unconscious, medical assistance must always be sought. GlucaGen® may have been prescribed so that members of your household can give the injection if you become hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) and are unable to take sugar by mouth. If you are unconscious, GlucaGen® can be given while awaiting medical assistance.
Show your family members and others where you keep this kit and how to use it. They need to know how to prepare it before you need it. They can practice giving a shot by giving you your normal insulin shots. It is important that they practice. A person who has never given a shot probably will not be able to do it in an emergency.
IMPORTANT
- Act quickly. Prolonged unconsciousness may be harmful.
- These simple instructions will help you give glucagon successfully.
- Turn patient on his/her side to prevent choking.
- The content of the syringe does not contain glucagon. You must mix the contents of the syringe with the glucagon in the accompanying bottle before giving injection. (see DIRECTIONS FOR USE)
- Do not mix GlucaGen® until you are ready to use it.
- Discard any unused portion.
- Become familiar with the technique of preparing glucagon before an emergency arises.
- WARNING: THE PATIENT MAY BE IN A COMA FROM SEVERE HYPERGLYCEMIA (HIGH BLOOD SUGAR) RATHER THAN HYPOGLYCEMIA (LOW BLOOD SUGAR). IN SUCH A CASE, THE PATIENT WILL NOT RESPOND TO GLUCAGON AND REQUIRES IMMEDIATE MEDICAL ATTENTION.
INDICATION FOR USE
GlucaGen® is used to treat severe hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) reactions which may occasionally occur in patients with diabetes. Symptoms of severe hypoglycemic reactions include disorientation, loss of consciousness, and seizures. You should only give GlucaGen® injection if (1) the patient is unconscious, (2) the patient is having a seizure, or (3) the patient is disoriented and unable to eat sugar or a sugar-sweetened product. Milder cases of hypoglycemia should be treated promptly by eating sugar or a sugar-sweetened product such as a regular soft drink or fruit juice. GlucaGen® does not work if it is taken by mouth.
DIRECTIONS FOR USE:
To Prepare GlucaGen® For Injection:
Use the enclosed prefilled disposable syringe with the attached needle to reconstitute GlucaGen® before giving the injection.
Step 1. Take off the orange plastic cap off the vial. Pull the needle cover off the syringe. Insert the needle through the rubber stopper of the vial containing GlucaGen® and inject all the liquid from the syringe into the vial.
Step 1
Step 2. Without taking the syringe with a needle out of the vial, gently shake the vial in your hand until the powder has completely dissolved, and the solution is clear.

Step 2
Step 3. While the needle is still inside the vial, turn the vial upside down and while keeping the needle in the liquid, slowly withdraw all the liquid into the syringe. Be careful not to pull theplunger out of the syringe. This will also help minimize the leakage of the fluid around the syringe. The usual dose for adult and children weighing more than 55 lbs is 1 mg (1 ml). Therefore, withdraw the solution to 1 ml mark on the syringe. The usual dose for children weighing less than 55 lb is 0.5 mg (1/2 adult dose). Therefore, withdraw ½ of the solution from the vial (0.5 ml mark on the syringe) for these children. DISCARD UNUSED PORTION.

Step 3
To Inject GlucaGen®
Step 4. Turn the patient on his/her side. When an unconscious person awakens, he/she may vomit. Turning the patient on his/her side will prevent him/her from choking. Without removing the needle from the vial and while keeping the needle in the liquid, remove any air bubble(s) in the syringe by flicking the syringe with your finger and squirting any air bubbles out of the needle into the vial. Continue pushing the plunger until you have the correct dose as described in Step 3. In the event the plunger is pushed below the required dose, pull back the plunger until you have the correct dose. When you have a correct amount of glucagon in the syringe, pull the syringe with a needle from the vial. Insert the needle into the loose tissue under the injection site, and inject the glucagon solution. THERE IS NO DANGER OF OVERDOSE.

Step 4
After Giving the Injection
Step 5. Withdraw the needle and press on the injection site. Used syringe and needle should be placed in sharps containers (such as red biohazard containers), hard plastic containers (such as detergent bottles), or metal containers (such as an empty coffee can). Such containers should be sealed and disposed of properly.
Step 6. FEED THE PATIENT AS SOON AS HE/SHE AWAKENS AND IS ABLE TO SWALLOW. Give the patient a fast-acting source of sugar (such as a regular soft drink or fruit juice) and a long-acting source of sugar (such as crackers and cheese or a meat sandwich). If the patient does not awaken within 15 minutes, give another dose of GlucaGen® and INFORM A DOCTOR OR EMERGENCY SERVICES IMMEDIATELY.
Step 7. Even if the GlucaGen® awakens the patient, his/her doctor should be promptly notified. A doctor should be notified whenever severe hypoglycemic reactions happen.
How GlucaGen® Works
GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection) is quickly absorbed after injection under the skin or into the muscle. Glucagon action causes glucose (sugar) to be released from the liver where it is stored as glycogen. Blood sugar levels increase within 10 minutes of injection and reach the highest amount approximately half an hour after injection. Glucagon works by promoting the release of glycogen (stored sugar in the liver).
When GlucaGen® Should Not Be Used
Do not use GlucaGen® if a patient is allergic to glucagon.
WARNINGS
Hypoglycemia may occur again following glucagon treatment. Tell your friends or relatives that you must be given a fast-acting source of sugar (such as regular soft drink or fruit juice), followed by a long acting source of sugar (carbohydrates) by mouth as soon as you are able to take it after you have responded to treatment - this will prevent the return of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). Early symptoms of hypoglycemia may include:
- perspiration
- drowsiness
- dizziness
- sleep disturbances
- palpitation
- anxiety
- tremor
- blurred vision
- hunger
- slurred speech
- restlessness
- depressed mood
- tingling in the hands, feet, lips, or tongue
- irritability
- abnormal behavior
- lightheadedness
- unsteady movement
- inability to concentrate
- personality changes
- headache
Allergic reactions may occur rarely and include generalized rash, anaphylactic shock, breathing difficulties and hypotension (low blood pressure).
Keep this kit out of reach of children.
PRECAUTIONS
General - GlucaGen® is only of benefit in hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) when the liver has sufficient glucose (in the form of glycogen) to release. For that reason GlucaGen® has little or no effect if you are fasting, or if you are suffering from adrenal insufficiency, chronic hypoglycemia or alcohol induced hypoglycemia. Remember GlucaGen® has the opposite effect of insulin.
If the GlucaGen solution shows any sign of gel formation or particles it should be discarded.
Your GlucaGen® HypoKit for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) includes:
- One vial of 1 mg GlucaGen® (glucagon [rDNA origin] for injection)
- One prefilled disposable syringe with attached needle containing 1 ml Sterile Water for Reconstitution
The vial has a protective plastic cap. You must remove the plastic cap to inject the water and reconstitute the freeze-dried GlucaGen®. If the cap is loose or missing when you buy the package, return it to your local pharmacy.
Pregnancy - GlucaGen® is glucagon which is a hormone that is always present in humans. GlucaGen® is intended for infrequent use during acute, severe hypoglycemic attacks, and may be used during pregnancy.
Nursing Mothers - Breast feeding following treatment with GlucaGen® for your hypoglycemic attack should not put your baby at risk. GlucaGen® does not stay very long in the body. Also, because glucagon is a protein, even if the infant ingested glucagon, it would be unlikely to have any effect on the infant because it would be digested.
POSSIBLE PROBLEMS WITH GlucaGen® TREATMENT
Severe side effects are very rare, although nausea and vomiting may occur occasionally. Side effects indicating toxicity of GlucaGen® have not been reported.
A few people may be allergic to glucagon or to one of the inactive ingredients in GlucaGen®, or may experience rapid heart beat for a short while.
If you experience any other reactions which are likely to have been caused by GlucaGen®, please contact your doctor.
EXPIRATION DATE
Before mixing - The GlucaGen® package may be stored up to 24 months at controlled room temperature 20o to 25o C (68o to 77o F) prior to reconstitution. Avoid freezing and protect from light. Never use GlucaGen® after the expiration date printed on the package. GlucaGen® does not contain preservatives and is for single use only.
After mixing - Reconstituted GlucaGen® should be used immediately. Discard any unused portion.
GlucaGen® is a registered trademark of Novo Nordisk A/S
© Novo Nordisk A/S, 2005
For information contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
Princeton, New Jersey 08540
1-800-727-6500
www.novonordisk-us.com
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk® A/S
2880 Bagsvaerd, Denmark
Last Updated: 11/05
GlucaGen, glucagon hydrochloride, patient information (in plain English)
Detailed Info on Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments of Diabetes
The information in this monograph is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects. This information is generalized and is not intended as specific medical advice. If you have questions about the medicines you are taking or would like more information, check with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
back to: Browse all Medications for Diabetes
APA Reference
Staff, H.
(2005, November 1). GlucaGen for Diabetics - GlucaGen Full Prescribing Information, HealthyPlace. Retrieved
on 2026, March 3 from https://www.healthyplace.com/diabetes/medications/glucagen-glucagon-hydrochloride