Ritalin (Methylphenidate) Patient Information
Find out why Ritalin is prescribed, side effects of Ritalin, Ritalin warnings, effects of Ritalin during pregnancy, more - in plain English.
Generic name: Methylphenidate hydrochloride
Brand names: Ritalin, Concerta, Metadate, Methylin
Pronounced: RIT-ah-lin
Full Ritalin Prescribing Information
Why is Ritalin prescribed?
Ritalin and other brands of methylphenidate are mild central nervous system stimulants used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children. With the exception of Ritalin LA, Concerta and Metadate CD, these products are also used in adults to treat narcolepsy (an uncontrollable desire to sleep).
When given for attention deficit disorder, this drug should be an integral part of a total treatment program that includes psychological, educational, and social measures. Symptoms of attention deficit disorder include continual problems with moderate to severe distractibility, short attention span, hyperactivity, emotional changeability, and impulsiveness.
Most important fact about Ritalin
Excessive doses of this drug over a long period of time can produce addiction. It is also possible to develop tolerance to the drug, so that larger doses are needed to produce the original effect. Because of these dangers, be sure to check with your doctor before making any change in dosage; and withdraw the drug only under your doctor's supervision.
How should you take Ritalin?
Follow your doctor's directions carefully. It is recommended that methylphenidate be taken 30 to 45 minutes before meals. If the drug interferes with sleep, give the child the last dose before 6 p.m. Ritalin-SR, Ritalin LA, Metadate CD, Methylin ER, and Concerta are long-acting forms of the drug, taken less frequently. They should be swallowed whole, never crushed or chewed. (Ritalin LA and Metadate CD may also be given by sprinkling the contents of the capsule on a tablespoon of cool applesauce and administering immediately, followed by a drink of water.)
--If you miss a dose...
Give it to the child as soon as you remember. Give the remaining doses for the day at regularly spaced intervals. Do not give 2 doses at once.
--Storage instructions...
Keep out of reach of children. Store below 86 degrees Fahrenheit in a tightly closed, light-resistant container. Protect Ritalin-SR from moisture.
What side effects may occur when taking Ritalin?
Side effects cannot be anticipated. If any develop or change in intensity, inform your doctor as soon as possible. Only your doctor can determine if it is safe for you to continue giving this drug.
- More common side effects of Ritalin may include: Inability to fall or stay asleep, nervousness
These side effects can usually be controlled by reducing the dosage and omitting the drug in the afternoon or evening.
In children, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, weight loss during long-term therapy, inability to fall or stay asleep, and abnormally fast heartbeat are more common side effects.
- Less common or rare side effects may include: Abdominal pain, abnormal heartbeat, abnormal muscular movements, blood pressure changes, chest pain, dizziness, drowsiness, fever, hair loss, headache, hives, jerking, joint pain, loss of appetite, nausea, palpitations (fluttery or throbbing heartbeat), pulse changes, rapid heartbeat, reddish or purplish skin spots, skin reddening, skin inflammation with peeling, skin rash, Tourette's syndrome (severe twitching), weight loss during long-term treatment
Why should Ritalin not be prescribed?
This drug should not be prescribed for anyone experiencing anxiety, tension, and agitation, since the drug may aggravate these symptoms.
Anyone sensitive or allergic to this drug should not take it.
This medication should not be taken by anyone with the eye condition known as glaucoma, anyone who suffers from tics (repeated, involuntary twitches), or someone with a family history of Tourette's syndrome (severe and multiple tics).
This drug is not intended for use in children whose symptoms may be caused by stress or a psychiatric disorder.
This medication should not be used for the prevention or treatment of normal fatigue, nor should it be used for the treatment of severe depression.
This drug should not be taken during treatment with drugs classified as monoamine oxidase inhibitors, such as the antidepressants Nardil and Parnate, nor for the 2 weeks following discontinuation of these drugs.
Special warnings about Ritalin
Your doctor will do a complete history and evaluation before prescribing this drug. He or she will take into account the severity of the symptoms, as well as your child's age.
This drug should not be given to children under 6 years of age; safety and effectiveness in this age group have not been established.
There is no information regarding the safety and effectiveness of long-term treatment in children. However, suppression of growth has been seen with the long-term use of stimulants, so your doctor will watch your child carefully while he or she is taking this drug.
Blood pressure should be monitored in anyone taking this drug, especially those with high blood pressure.
Some people have had visual disturbances such as blurred vision while being treated with this drug.
The use of this drug by anyone with a seizure disorder is not recommended. Be sure your doctor is aware of any problem in this area. Caution is also advisable for anyone with a history of emotional instability or substance abuse, due to the danger of addiction.
Possible food and drug interactions when taking Ritalin
 If this medication is taken with certain other drugs, the effects of either can be increased, decreased, or altered. It is especially important to check with your doctor before combining this drug with the following:
If this medication is taken with certain other drugs, the effects of either can be increased, decreased, or altered. It is especially important to check with your doctor before combining this drug with the following:
Antiseizure drugs such as phenobarbital, Dilantin and Mysoline
Antidepressant drugs such as Tofranil, Anafranil, Norpramin, and Effexor
Blood thinners such as Coumadin
Clonidine (Catapres-TTS)
Drugs that restore blood pressure, such as EpiPen
Guanethidine (Ismelin)
MAO inhibitors (drugs such as the antidepressants Nardil and Parnate)
Phenylbutazone
Special information if you are pregnant or breastfeeding
The effects of Ritalin during pregnancy have not been adequately studied. If you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant, inform your doctor immediately. It is not known if this drug appears in breast milk. If this medication is essential to your health, your doctor may advise you to discontinue nursing your baby until your treatment with this medication is finished.
Recommended dosage for Ritalin
 ADULTS
ADULTS
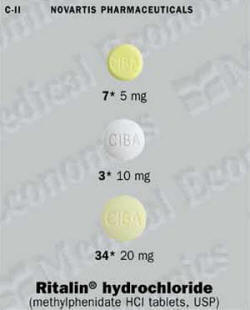
Ritalin and Methylin Tablets
The average dosage is 20 to 30 milligrams a day, divided into 2 or 3 doses, preferably taken 30 to 45 minutes before meals. Some people may need 40 to 60 milligrams daily, others only 10 to 15 milligrams. Your doctor will determine the best dose.
Ritalin-SR, Methylin ER, and Metadate ER Tablets
These tablets keep working for 8 hours. They may be used in place of Ritalin tablets if they deliver a comparable dose over an 8-hour period.
CHILDREN
This drug should not be given to children under 6 years of age.
Ritalin and Methylin Tablets
The usual starting dose is 5 milligrams taken twice a day, before breakfast and lunch; your doctor will increase the dose by 5 to 10 milligrams a week. Your child should not take more than 60 milligrams in a day. If you do not see any improvement over a period of 1 month, check with your doctor. He or she may wish to discontinue the drug.
 Ritalin-SR, Methylin ER, and Metadate ER Tablets
Ritalin-SR, Methylin ER, and Metadate ER Tablets
These tablets continue working for 8 hours. Your doctor will decide if they should be used in place of the regular tablets.
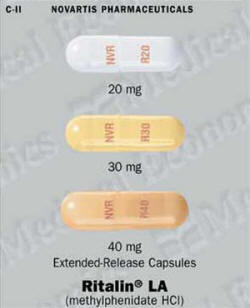
Ritalin LA Capsules
The recommended starting dose is 20 milligrams once daily in the morning. At weekly intervals, the doctor may increase the dose by 10 milligrams, up to a maximum of 60 milligrams once a day.
Concerta Tablets
The recommended starting dose is 18 milligrams once daily in the morning. At weekly intervals, your doctor may increase the dose in 18-milligram steps, up to a maximum of 54 milligrams each morning.
Metadate CD Capsules
The recommended starting dose is 20 milligrams once daily before breakfast. If necessary, the doctor may increase the dose in 20-milligram steps to a maximum of 60 milligrams once a day.
Your doctor will periodically discontinue the drug in order to reassess your child's condition. Drug treatment should not, and need not, be indefinite and usually can be discontinued after puberty.
Overdosage of Ritalin
If you suspect an overdose of Ritalin, seek medical attention immediately.
Symptoms of Ritalin overdose may include: Agitation, confusion, convulsions (may be followed by coma), delirium, dryness of mucous membranes, enlarging of the pupil of the eye, exaggerated feeling of elation, extremely elevated body temperature, flushing, hallucinations, headache, high blood pressure, irregular or rapid heartbeat, muscle twitching, sweating, tremors, vomiting
Full Ritalin Prescribing Information
Detailed Info on Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Treatments of ADHD
APA Reference
Staff, H.
(2009, January 3). Ritalin (Methylphenidate) Patient Information, HealthyPlace. Retrieved
on 2026, January 18 from https://www.healthyplace.com/other-info/psychiatric-medications/ritalin-methylphenidate-patient-information